Loose teeth are not such a big deal when you’re a kid. It generally means you’d get a visit from the tooth fairy soon and you get to whistle through the gap. But as adults, loose adult/permanent teeth is a big warning that something wrong is happening in the mouth or in the body. We’ve listed some common causes of tooth mobility below.
All Gummed Up
Periodontal disease is the most common culprit of loose teeth as it not only affects your gums but the ligaments and bone that are the structure and support holding your teeth in place. When plaque builds up around the tooth, the bacterial toxins that are released inflame the gum.
There is bleeding at the gum line, as well as your gum actually pulling away from the tooth itself. It’s a bad cycle of bacteria going into your gum pocket and widening it, allowing more bacteria to get into that pocket.
Before periodontal disease becomes extreme, take matters into your own hands by brushing and flossing regularly and consistently. Up your oral hygiene game and it will improve. However, if it does get chronic, definitely speak to your dentist as they will be able to prescribe the most appropriate course of action.
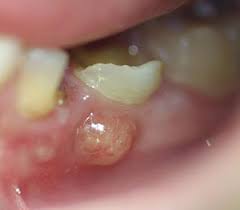
Abyss in the Abscess
On the extreme end of gum disease and tooth decay, abscesses can form at the end of a tooth root and eat away at the tooth structure. All the bacterial infection has to accumulate somewhere. Most commonly it accumulates in the soft, dead/dying nerve of the tooth before leaching to the root apex (periapical abscess). In other instances, the pus collects within the soft tissues (the surrounding gum and ligaments) that hold up the tooth (periodontal abscess).
In both cases, abscesses can cause resorption of the bone and consequently the tooth slowly detaches from all supportive structures (bone, gum, ligaments). Sometimes, this abscess and detachment may be treatable, other times, it is permanent, so consult your dentist regarding their diagnosis and recommended treatment.
Grind to a Halt
Bruxism is involuntary, forceful, and habitual teeth grinding and jaw clenching. Severe or chronic bruxism can actually cause tooth detachment and mobility as the grinding applies so much pressure to the teeth that it starts to shift them. The good news is, tooth mobility due to bruxism is generally reversible once the bruxism is managed properly.
A Traumatic Situation
Of course, if your mouth and teeth sustain a trauma (such as an elbow to the face during a contact sport or a punch from a fight), this could cause sudden tooth mobility. The injury may damage the periodontium and nearby soft tissues (thereby loosening the tooth) or severely fracture the tooth. It is always recommended to see your dentist as soon as possible whenever you sustain a dental trauma so they can treat it and hopefully get you out of pain.
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, women experience high levels of progesterone and estrogen. These high levels can temporarily loosen the ligaments and bone around your teeth during the pregnancy but shouldn’t lead to any long-term issues. If you’re concerned about your loose teeth during your pregnancy, you should speak to your dentist and they’ll be able to gauge whether it is normal or if you’re sustaining complicating factors.

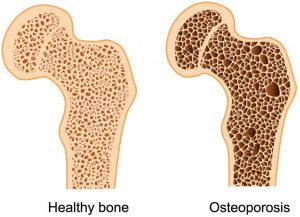
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition in which the bones throughout the body become less dense and are prone to fracture. It follows that when the bone density around your teeth lessens, your teeth loosen. Women who suffer from osteoporosis are three times more likely to experience tooth loss than women without the disease. Speak with your dental and medical practitioners to find out how to treat your osteoporosis.